Parallel structure adds both clout (prestige /βαρύτητα) and clarity to your writing.
When you use parallel structure, you increase the
readability of your writing by creating word patterns readers can follow easily.
Understanding Parallel Structure
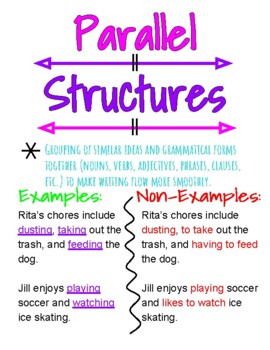
Parallel structure (also called parallelism) is the repetition of a chosen grammatical form within a sentence. By
making each compared item or idea in your sentence follow the same grammatical pattern, you create a parallel
construction.
Example
Not Parallel:
Ellen likes hiking, the rodeo, and to take afternoon naps.
Parallel:
Ellen likes hiking, attending the rodeo, and taking afternoon naps.
OR
Ellen likes to hike, attend the rodeo, and take afternoon naps.
Using Parallel Structure
With Coordinating Conjunctions
When you connect two or more clauses or phrases with a coordinating conjunction (for, and, nor, but,
or, yet, or so), use parallel structure.
Example
Not Parallel:
My best friend took me dancing and to a show.
Parallel:
My best friend took me to a dance and a show.
With Correlative Conjunctions (σύνδεσμος)
When you connect two clauses or phrases with a correlative (συσχετικός) conjunction (not only…but also, either…or,
neither…nor, if…then, etc.), use parallel structure.
Example
Not Parallel:
My dog not only likes to play fetch, but also chase cars.
Parallel:
My dog not only likes to play fetch, but he also likes to chase cars.
OR
My dog likes not only to play fetch, but also to chase cars.
With Phrases or Clauses of Comparison (δευτερεύουσες προτάσεις σύγκρισης)
When you connect two clauses or phrases with a word of comparison, such as than or as, use parallel
structure.
Example
Not Parallel:
I would rather pay for my education than financial aid.
Parallel:
I would rather pay for my education than receive financial aid.
With Lists
When you are comparing items in a list, use parallel structure.
Example
Not Parallel:
John Taylor Gatto criticizes public schools because they are compulsory, funded
by the government, and destroy students' humanity.
Parallel:
John Taylor Gatto criticizes public schools because they are compulsory, governmentfunded, and normalizing.
OR
John Taylor Gatto criticizes public schools because they require students to attend,
receive money from the government, and destroy students' humanity.
_______________________________________
Online exercises:
http://www.wilbers.com/part36.htm
https://www.learngrammar.net/practice/47/exercise-on-parallel-structure-with-explanation